Chemistry Paper-2 2021 — CSS Past Paper
FEDERAL PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION
COMPETITIVE EXAMINATION-2021
FOR RECRUITMENT TO POSTS IN BS-17
UNDER THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT
CHEMISTRY, Paper-2
TIME ALLOWED: THREE HOURS
PART-I(MCQS): MAXIMUM 30 MINUTES
PART-I (MCQS) MAXIMUM MARKS = 20
PART-II MAXIMUM MARKS = 80
NOTE:
- (i) Part-II is to be attempted on the separate Answer Book.
- (ii) Attempt ONLY FOUR questions from PART-II. ALL questions carry EQUAL marks.
- (iii) All the parts (if any) of each Question must be attempted at one place instead of at different places.
- (iv) Candidate must write Q. No. in the Answer Book in accordance with Q. No. in the Q.Paper.
- (v) No Page/Space be left blank between the answers. All the blank pages of Answer Book must be crossed.
- (vi) Extra attempt of any question or any part of the attempted question will not be considered.
PART-II
Q. No. 2.
(a) Describe factors that influence keto-enol tautomerization. Elaborate the statement with the help of examples. (10)
(b) Assign “R- or **S” configuration on each of the chiral centres of the given compounds. (10) (20)
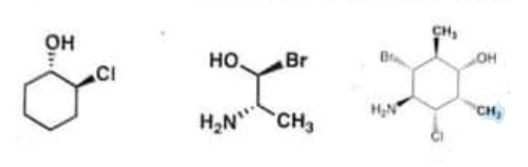
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 2 b, CSS 2021
Q. No. 3.
Give the products expected (if any) when ethylbenzene reacts under following conditions: (02 marks each)
(i) Br, in CCI4 (dark) ( In)
(ii) 1-1N0,1-1,S0,
(iii) Conc. 11:SO,
(iv)
0 c2HiA-ci .A1C1,(1 I equi, ). then H2O
(v) Alkaline KMnO4
(b) Account for the following: (05 marks each) (10) (20)
(i) Intramolecular II-bonding is stronger than intermolecular H-bonding
(ii) Control of nucleophilic substitution reaction over elimination reactions
Q. No. 4.
(a) Write down reagents, reaction conditions and important steps for the following conversions: (10)
(i) Chlorobenzene to 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
(ii) Pyridine, to 2-ammo pyridine
(b) Write a note that substituents on aromatic rings dictate reactivity and orientation of the incoming electrophile in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. (10)
Q. No. 5.
Draw detailed mechanisms for:
(i)
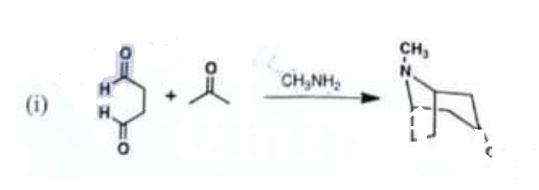
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 5 a, CSS 2021
(ii)
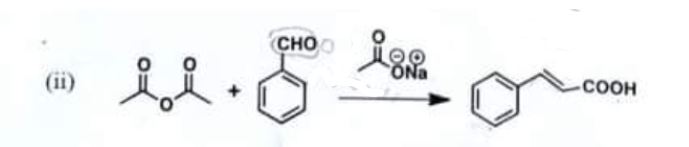
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 5 b, CSS 2021
(iii)
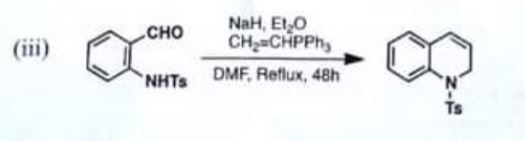
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 5 c, CSS 2021
(iv)
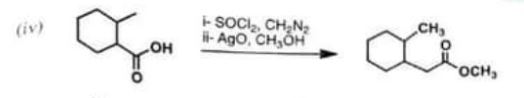
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 5 d, CSS 2021
(v)
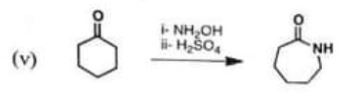
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 5 e, CSS 2021
Q. No. 6.
Account for the following: (05 marks each)
(I) In DNA. a guanine residue reacts with electrophiles predominantly at the 7 and 3 positions of the ring system (see below). Suggest an explanation for this.
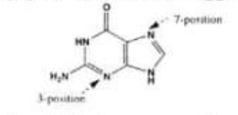
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 6 a, CSS 2021
(ii) Outline the synthesis of following compound:
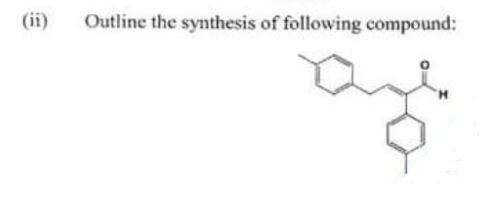
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 6 b, CSS 2021
(iii) A Grignard reagent that is a key intermediate in an industrial synthesis of vitamin A can be synthesized in the following way:
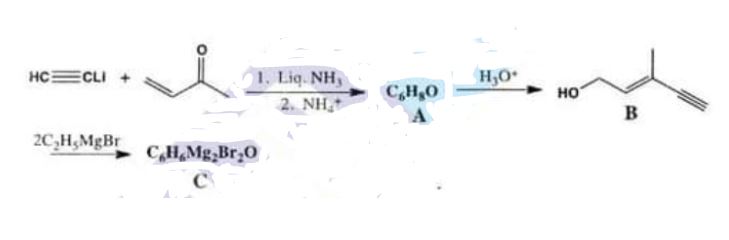
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 6 c, CSS 2021
What are the structures of compounds A and C? The acid catalysed rearrangement of A to B takes pl.
(iv) What are compounds A and B in the reaction given below? Compound B has a strong IR absorption band in the 1650-1730 cm-I region and a broad strong band in the 3200 3550 cm’ region. (20)
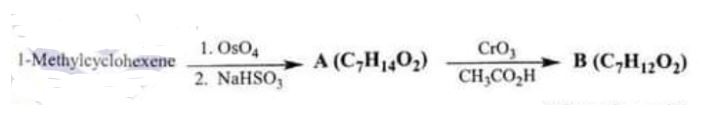
Chemistry, Paper 2, Q 6 d, CSS 2021
Q. No. 7.
Explain the following: (04 marks each) (20)
(i) How can ER be used to help interpret NMR spectra?
(ii) What are diastereotopic protons? Explain with examples.
(iii) Determine the structure for a compound with formula C61-14N204 with following 1H-NMR data: 8.761(114), 8.38 dd (2H), 7.97 1(1H)
(iv) Assign chemical shifts of each proton in the above structure.
(v) Why 13C-NMR is less sensitive than IH-NMR?
Q. No. 8.
Answer following questions: (04 marks each) (20)
- (i) Comment if glycogenesis is anabolic or catabolic. Write down all steps involve in glycogenesis.
- (ii) Describe endergonic and endergonic reactions
- (iii) Write a note on anionic and cationic surfactants.
- (iv) Comment if waste glass can be used for cement production.
- (v) What is the chemical composition of nucleic acids and their biological significance?
**********